Burns happen fast- but with the right treatment, so can healing. Whether it’s a kitchen mishap, a sparky plug or a chemical spill, knowing how to respond can make all the difference. In this feature, we will explore protocols and quick-action tips to counter burns.
THERMAL or HEAT BURNS:
Thermal burns are caused by contact with hot surfaces, liquids, steam and most commonly, open flames. Sunburns are also thermal burns and can cause severe skin damage.
STEP 1:
- The first and most crucial step is to stop the burning process by removing the source of heat.
- In case of exposure to hot surfaces, liquids or steam, remove any clothing or jewellery that is stuck to skin. Do NOT attempt to remove anything that is stuck to the skin.
- If a person’s clothing catches fire, instruct them to ‘’stop, drop and roll’’ or use a blanket to smother the flames.
- Use an appropriate fire extinguisher to put out the fire
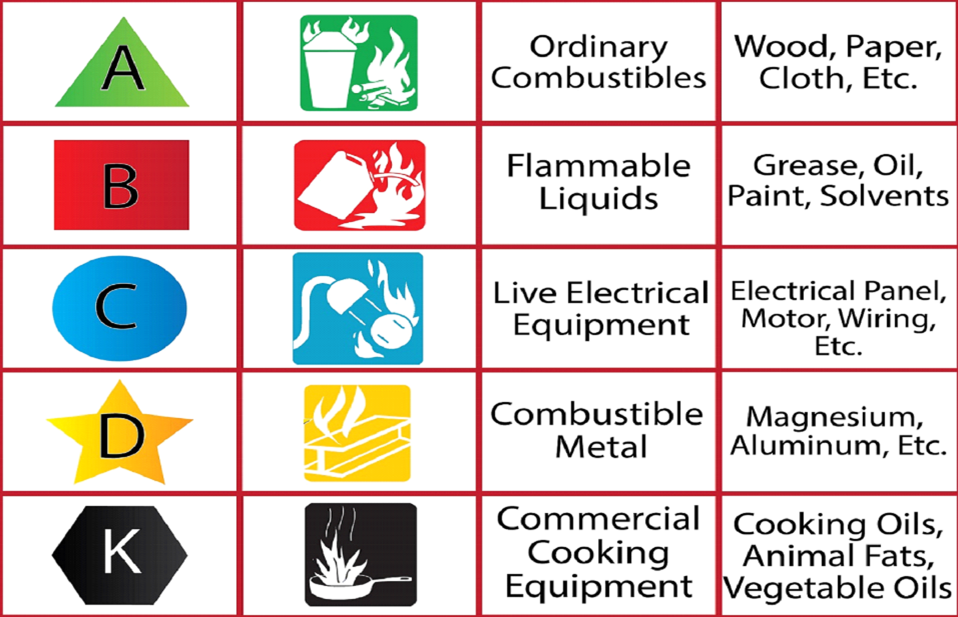
If you find this hard to remember, we have an easy way for you to remember it.
| Class A What’s burning? Wood, paper. When you burn wood or paper it leaves Ash. A is for Ash | Class B What’s burning? Liquids (petroleum). When you heat up liquids on the stove they Boil. B is for Boil. | Class C What’s burning? Electrical. Electricity has Current. C is for Current. | Class D What’s burning? Metal. If you hit your metal truck with a hammer it puts a Dent in it. D is for Dent. | Class K What’s burning? Cooking oils, animal fats. Just like at KFC (or in your Kitchen). K is for KFC |
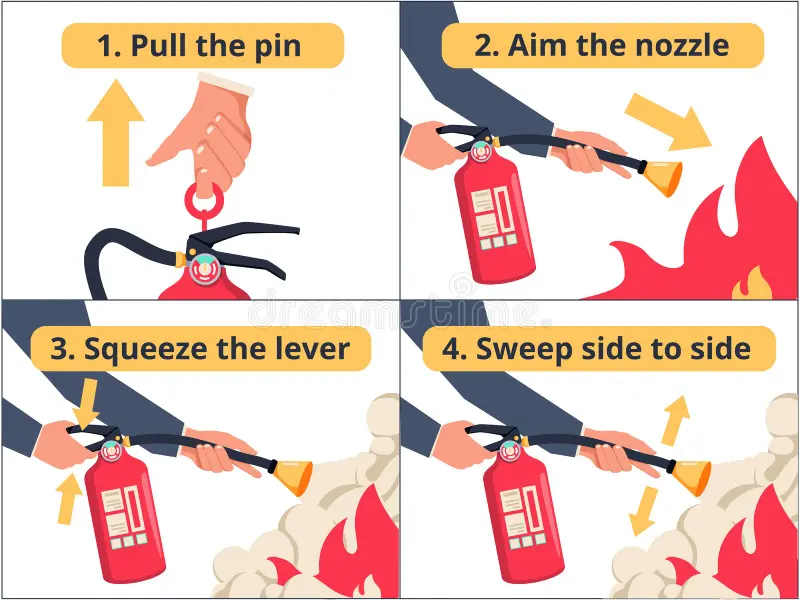
Ensure that you have an exit route before using a fire extinguisher. To use the fire extinguisher, remember the PASS technique when using a fire extinguisher
P – Pull the pin in the handle
A – Aim the nozzle at the base of the fire
S – Squeeze the lever
S – Sweep from side to side
In case of a major fire, pull the alarm and call the helpline for fire brigade (101 or 112 in India)
If there are any casualties, dial 108 or 102 to call an ambulance.
STEP 2:
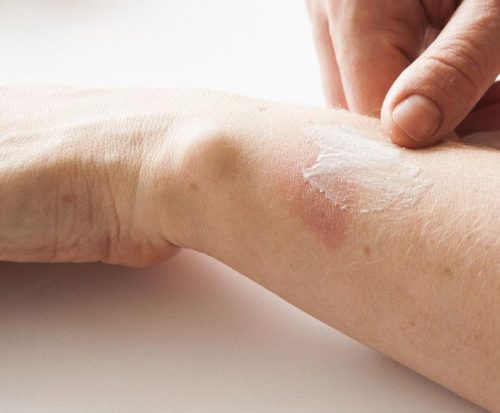
If it’s a minor burn ( redness, pain and swelling on a small part of the body)
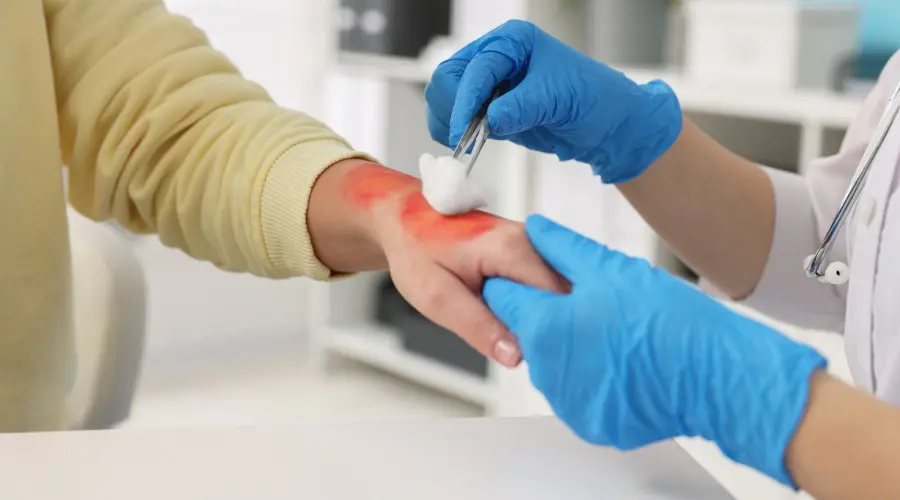
- Cool the burn by running it under lukewarm or cool water (not ice-cold) for 10-20 minutes. Do NOT use ice or iced water as it can restrict blood flow and cause more damage to the area. If running water is not available, use a cold, wet cloth.
- For facial burns, gently apply a cool, damp cloth until the pain subsides. For a mouth burn from hot food or drink, put a piece of ice in the mouth for a few minutes.
- Once the burn has cooled, apply a lotion such as aloe vera or cocoa butter and bandage the area
- Over-the-counter pain relievers such as Paracetamol or Ibuprofen can help manage discomfort.
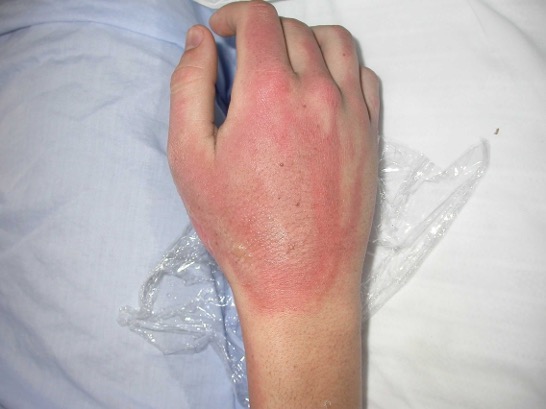
If it’s a major burn:
- Ensure that the burned person is breathing. If needed, begin rescue breathing
- Remove clothes, jewellery, belts and other tight items, especially from the burned area and the neck. Burned areas swell quickly
- Cover the burn. Loosely cover the area with gauze or a clean cloth.
- If possible, elevate the burned area above heart level to reduce swelling.
- Be alert for signs of shock such as cool, clammy skin, a weak pulse and shallow breathing. Call emergency services immediately if these symptoms appear.
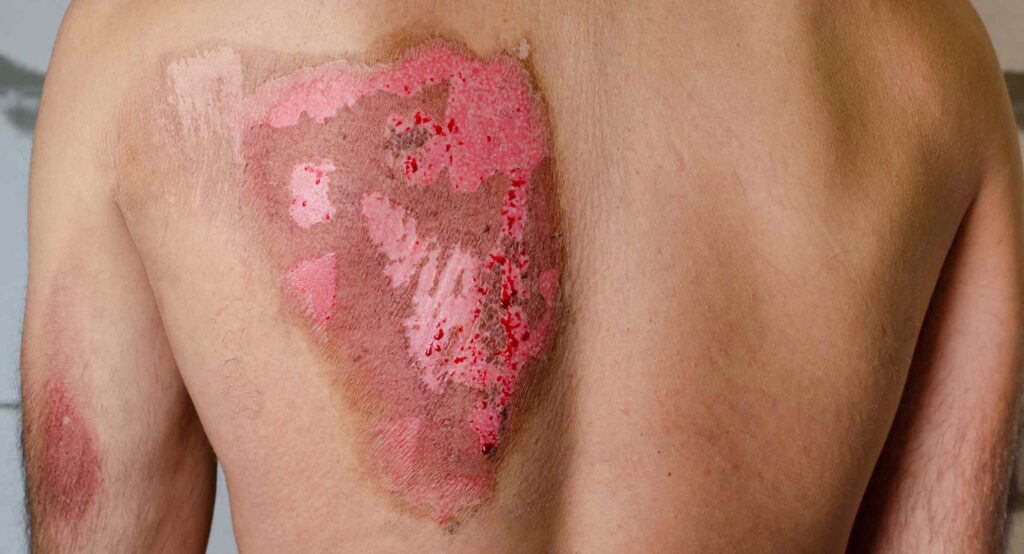
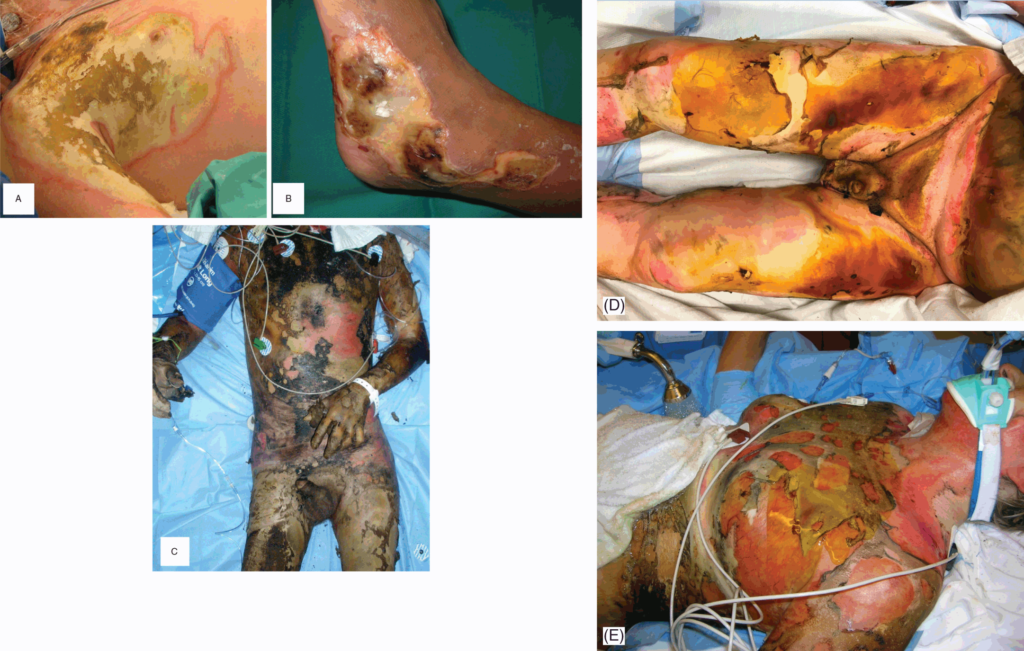
WHEN TO SEEK EMERGENCY HELP?
Call 108 or seek immediate care for major burns, which:
- May be deep, involving all layers of the skin.
- May cause the skin to be dry and leathery.
- May appear charred or have patches of white, brown or black.
- Are larger than 3 inches (about 8 centimeters) in diameter.
- Cover the hands, feet, face, groin, buttocks or a major joint, or encircle an arm or a leg.
- Are accompanied by smoke inhalation.
- Begin swelling very quickly.
- Electrical burns, including those caused by lightning, and major chemical burns need emergency medical care.
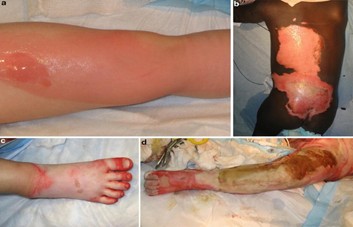
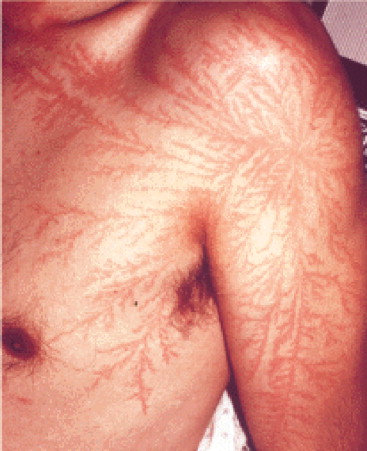
ELECTRICAL BURNS:
Electrical burns can be caused by electrical malfunction or even by lightning. Some symptoms of electrical burns include arrythmias, heart attack, seizures, muscle pain and contractions, trouble breathing.
STEP 1: In case of electrical burn, make sure the power source is off before you approach the burned person.
- Turn off the main power supply and unplug any cords before assisting the injured person.
- If that’s not possible, use material that does not conduct electricity, such as a dry wooden broom handle, to separate the person from the electricity source.
- Exercise extreme caution if the victim is in contact with water, as it conducts electricity.
- Avoid driving over or touching downed power lines
STEP 2: When it is safe, check if the person is conscious and breathing. Gently touch and talk to the person. If there is no response, start CPR.
If there is an electrical burn, you can treat it in the same way as you would any other burn: Put the burnt area under running water for at least 20 minutes then cover with a sterile gauze bandage or a clean cloth. Do NOT use a blanket or towel, because loose fibres can stick to the burns.
STEP 3: Go to the Hospital Emergency Department where they will run tests to check for heart or soft tissue damage.
CHEMICAL BURNS:
Chemical burns are commonly caused by battery acid, disinfectants, bleach, drain cleaners, dyes, fertilizers etc.
- Remove dry chemicals. Put on gloves and brush off any remaining material.
- Remove contaminated clothing or jewelry and rinse chemicals off for at least 20 minutes, in a shower if it’s available. Protect eyes from the chemicals. If the chemicals enter your eyes, rinse with water for 15-20 minutes while keeping your eyelids open
- If a chemical is ingested, drink plenty of water to help dilute it. Seek medical help immediately.
HOW TO TAKE CARE OF YOUR BURN WOUND?
- Avoid popping blisters, as they protect against infection. If a blister breaks, gently clean the area with water and apply an antibiotic ointment.
- Clean the wound regularly and apply antibiotics like silver sulfadiazine prescribed by your doctor.
- If you haven’t had a tetanus shot in the past five years and the burn is deep, you may need a booster shot. Try to get this within 48 hours of the injury.
- Do not apply butter, toothpaste, eggs or other home remedies as this can cause infection.
- Cover the burn when going out in the cold or sun, especially if it’s on exposed areas like hands, arms, or face.
- If a burn isn’t healing or seems infected, seek medical attention
- In a fresh burn, if the skin is missing, do not apply any greasy creams or Vaseline.
- Silicone gel and Massage therapy are recommended for scar management.
- Scar treatment options include skin grafting, skin flap surgeries, dermabrasion, laser surgeries.
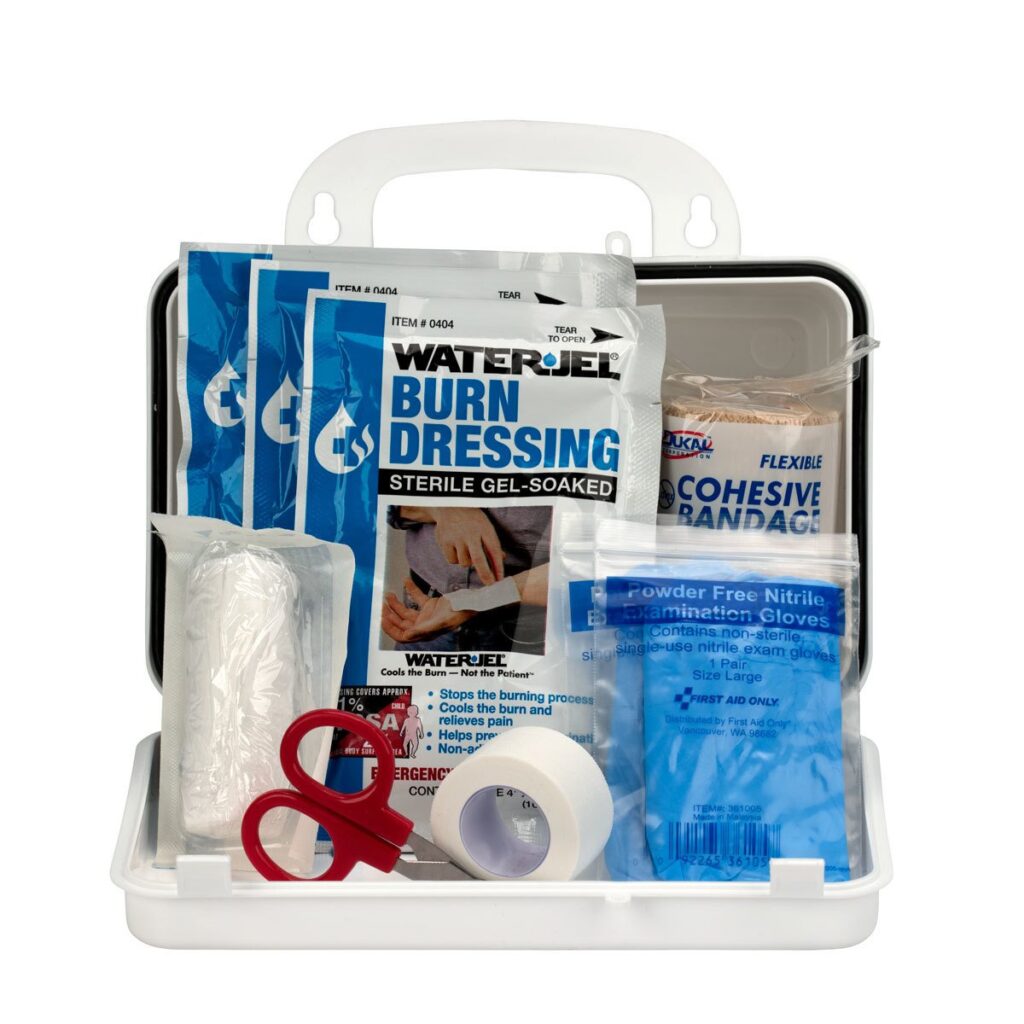
BURN FIRST-AID KIT ESSENTIALS
- Sterile saline solution(for rinsing burns)
- Burn gel or cooling burn dressings
- Aloe Vera gel
- Cold packs (never apply ice directly)
- Hydrogel sheets (helpful for cooling burns)
- Burn ointment (Ex: Silver sulfadiazine, antibiotic creams)
- Non- stick dressings
- Pain relievers (Paracetamol, Ibuprofen)

To summarize, systematic approach to burn care focuses on the six “Cs”: clothing, cooling, cleaning, chemoprophylaxis, covering and comforting (i.e., pain relief).
- Clothing: Remove any clothing from the burned area immediately.
- Cooling: Run cool water over the burn to reduce heat
- Cleaning: Wash the affected area with mild soap and water.
- Chemoprophylaxis: Apply topical antibiotic creams to prevent infection.
- Covering: Use sterile gauze or bandages to protect the wound.
- Comfort: Manage pain with appropriate pain relief medication.

Wow… Excellent Article.
Keep it up.
Very nice article. Excellent work.
Good job
What steps to be taken while different type’s of burn injuries was happened, written in simple language. Common people also understood the remedy. Ok keep going, may god bless you.
Nice article
So well written and easy to understand. Very well done.
I wish I found this earlier. Very nice selection of topic. Easy to understand
Amazing got to know so many things in a simple words,very well written.
This article is a must-read for everyone! Burns can happen anytime, and knowing how to react immediately can make all the difference. The way you’ve explained the different types of burns, emergency steps, and proper wound care is truly commendable. Thank you for providing such life-saving knowledge in such a clear and informative way!
Very informative article and the message brings awareness in people on burn injuries. Continue doing the good work. God bless you.
This kind of information can truly save lives! The detailed explanation of burn types, first aid, and emergency care is exactly what people need to be aware of. Your effort in spreading such crucial medical knowledge is highly appreciated. Keep up the great work!
Wow so informative
Neatly Explained!!!! Keep updating about Health concerns issues.
Well researched Article with Simple depiction. KUDOS
The article was very simple to understand with detailed insight. very informative. Hope you come up with more of such articles. well done.
This is amazing!
this article is amazing!
Very informative article
Very informative article well explained
Excellent article . Very useful to general public . Keep going Shreya .
Excellent article dear . Keep going .
Very informative and essential article which describes on unknown events with corrective measures are explained
Very informative article which helps to educate people on unknown events with corrective actions
A very informative read !!
Informative article, pleased to share this article to Others, Keep going
Information is very useful. Helps burn patients and civilians to take immediate action during burn injuries.
Good work as a medical student and nice topic to read and refresh. Congratulations.
Nice summary of burn injuries and their first aid treatment. Education about these events helps everyone know the scope of current practices and the path to recovery. But prevention is better than cure and emphasis on PPE when handling situations lie this is of atmost importance.
Good work!